Django ChatGPT Tutorial Series:
- Introduction
- Create Django Project with Modern Frontend Tooling
- Create Chat App
- Partial Form Submission With Turbo Frame
- Use Turbo Stream To Manipulate DOM Elements
- Send Turbo Stream Over Websocket
- Using OpenAI Streaming API With Celery
- Use Stimulus to Better Organize Javascript Code in Django
- Use Stimulus to Render Markdown and Highlight Code Block
- Use Stimulus to Improve UX of Message Form
- Source Code chatgpt-django-project
In this article, we will create a chat app, and relevant models, views and templates.
Chat App
Let's first create django app chat
# we put all django apps under the chatgpt_django_app
(venv)$ mkdir -p ./chatgpt_django_app/chat
(venv)$ python manage.py startapp chat ./chatgpt_django_app/chatWe will have structure like this
├── chatgpt_django_app
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── asgi.py
│ ├── settings.py
│ ├── chat # new
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── admin.py
│ │ ├── apps.py
│ │ ├── migrations
│ │ ├── models.py
│ │ ├── tests.py
│ │ └── views.py
│ ├── templates
│ │ └── index.html
│ ├── urls.py
│ └── wsgi.py
Update chatgpt_django_app/chat/apps.py to change the name to chatgpt_django_app.chat
from django.apps import AppConfig
class ChatConfig(AppConfig):
default_auto_field = 'django.db.models.BigAutoField'
name = 'chatgpt_django_app.chat' # updateAdd chatgpt_django_app.chat to the INSTALLED_APPS in chatgpt_django_app/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'chatgpt_django_app.chat', # new
]# check if there is any error
(venv)$ ./manage.py check
System check identified no issues (0 silenced).Model
Update chatgpt_django_app/chat/models.py
from django.db import models
class Chat(models.Model):
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
class Meta:
ordering = ["-created_at"]
class Message(models.Model):
SYSTEM = 0
ASSISTANT = 10
USER = 20
ROLE_CHOICES = (
(SYSTEM, "System"),
(ASSISTANT, "Assistant"),
(USER, "User"),
)
role = models.IntegerField(choices=ROLE_CHOICES)
chat = models.ForeignKey(Chat, on_delete=models.CASCADE, related_name="messages")
content = models.TextField()
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
class Meta:
ordering = ["created_at"]
@property
def role_label(self):
role_label = self.get_role_display()
return role_label
@classmethod
def for_openai(cls, messages):
return [
{"role": message.role_label.lower(), "content": message.content}
for message in messages
]Notes:
Chatmodel is used to group messagesrolefield of the message is used to distinguish the message is from system, assistant or user.
Migrate the db
(venv)$ python manage.py makemigrations
(venv)$ python manage.py migrateForm
Create chatgpt_django_app/chat/forms.py
from django import forms
from .models import Chat, Message
class MessageForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Message
fields = ("content",)
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.role = kwargs.pop("role")
self.chat_pk = kwargs.pop("chat_pk")
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
def save(self, commit=True):
instance = super().save(commit=False)
instance.chat_id = self.chat_pk
instance.role = self.role
if commit:
instance.save()
return instanceWe will use this form to create message in a bit.
View
Next, we will create views for the chat app.
Edit chatgpt_django_app/chat/views.py
from django.urls import reverse
from django.views import View
from django.views.generic.list import ListView
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from .models import Chat, Message
class IndexView(View):
def get(self, request):
# If no chat exists, create a new chat and redirect to the message list page.
chat = Chat.objects.first()
if not chat:
chat = Chat.objects.create()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse("chat:message-list", args=[chat.pk]))
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# create new chat object and redirect to message list view
instance = Chat.objects.create()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse("chat:message-list", args=[instance.pk]))
index_view = IndexView.as_view()
class MessageListView(ListView):
model = Message
template_name = "message_list_page.html"
def get_queryset(self):
qs = super().get_queryset()
qs = qs.filter(chat_id=self.kwargs["chat_pk"])
return qs
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
context = super().get_context_data(**kwargs)
context["chats"] = Chat.objects.all()
return context
message_list_view = MessageListView.as_view()Notes:
- When we visit the index page, we will create a new chat object if there is no chat object exists.
- If we send a POST request to the index page, we will create a new chat object and redirect to the message list page.
MessageListViewis to display all message for a chat. It will also display all chats in the sidebar, so user can switch to another chat.
Templates
Create chatgpt_django_app/templates/base.html
{% load webpack_loader static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>ChatGPT Demo</title>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
{% stylesheet_pack 'app' %}
{% javascript_pack 'app' attrs='defer' %}
</head>
<body>
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
</body>
</html>Notes:
- We move JS from the end of the body to the head element, and set
deferattribute. - If the
deferattribute is set, it specifies that the script is downloaded in parallel to parsing the page, and executed after the page has finished parsing
Create chatgpt_django_app/templates/message_list_page.html
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block content %}
<main class="w-full">
<div class="grid grid-cols-12 gap-2">
<div class="col-span-12 bg-gray-50 sm:col-span-3">
<div class="flex flex-col space-y-1 sm:h-screen">
<form method="post" action="{% url 'chat:index' %}">
{% csrf_token %}
<button type="submit" class="bg-green-500 text-white py-2 px-4 rounded m-2">Start a new conversation</button>
</form>
<ul class="flex flex-col py-4 space-y-2">
{% for chat in chats %}
<a class="text-white py-2 px-2 rounded mx-2 bg-blue-500"
href="{% url 'chat:message-list' chat.pk %}">Chat: created on <time>{{ chat.created_at }}</time></a>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-span-12 bg-gray-50 sm:col-span-9">
<div class="bg-gray-50 sm:h-screen">
<div class="flex flex-col h-full">
<!-- Message List -->
<div class="overflow-y-auto flex-1">
{% for instance in object_list %}
<div id="message_{{ instance.pk }}">
{% if instance.role_label == 'User' %}
<div class="p-4 m-4 max-w-full text-black rounded-lg bg-sky-100 prose" >{{ instance.content }}</div>
{% else %}
<div class="p-4 m-4 max-w-full bg-gray-200 rounded-lg prose">{{ instance.content }}</div>
{% endif %}
</div>
{% endfor %}
</div>
<!-- Message Form -->
<div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</main>
{% endblock %}Urls
Create chatgpt_django_app/chat/urls.py
from django.urls import path
from .views import (
index_view,
message_list_view,
)
app_name = "chat"
urlpatterns = [
path("chat/", index_view, name="index"),
path("chat/<int:chat_pk>/message/list/", message_list_view, name="message-list"),
]Update chatgpt_django_app/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('', include("chatgpt_django_app.chat.urls")), # new
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]Test
Let's run the app
$ npm run startAnd then run Django server
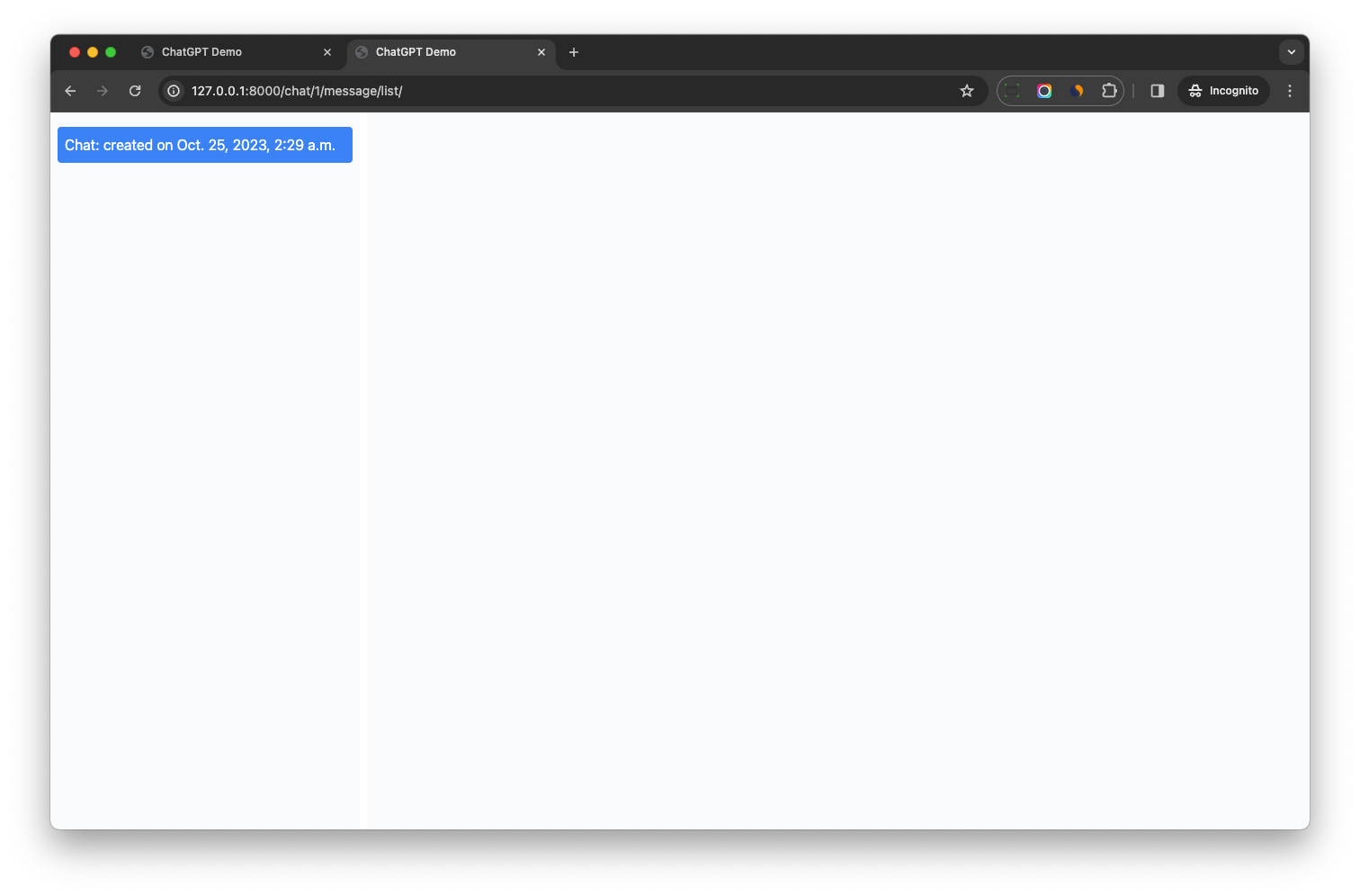
(venv)$ python manage.py runserverOpen http://localhost:8000/chat/ in your browser, we should see the message list page.
Django ChatGPT Tutorial Series:
- Introduction
- Create Django Project with Modern Frontend Tooling
- Create Chat App
- Partial Form Submission With Turbo Frame
- Use Turbo Stream To Manipulate DOM Elements
- Send Turbo Stream Over Websocket
- Using OpenAI Streaming API With Celery
- Use Stimulus to Better Organize Javascript Code in Django
- Use Stimulus to Render Markdown and Highlight Code Block
- Use Stimulus to Improve UX of Message Form
- Source Code chatgpt-django-project